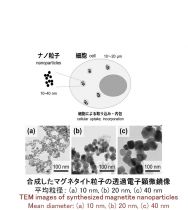
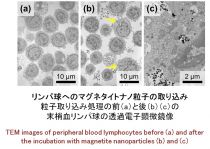
Development of magnetic nanoparticles for cancer care

- researcher's name
- affiliation
-
- research field
-
Device related chemistry,Nanobioscience,Electronic materials/Electric materials
- keyword
-
background
● Appropriate size for medical care, e.g. a suitable size for cellular uptake
● Appropriate magnetic properties, depending on size, for the treatment and diagnosis
● High biocompatibility and target specificity
● Appropriate magnetic properties, depending on size, for the treatment and diagnosis
● High biocompatibility and target specificity
summary
● Magnetite nanoparticles with the mean size tuned in the range of 10 to 40 nm
● High dispersibility of nanoparticles (modified with amine) in aqueous solution
● Use of cells containing nanoparticles in the treatment and diagnosis of cancer
● High dispersibility of nanoparticles (modified with amine) in aqueous solution
● Use of cells containing nanoparticles in the treatment and diagnosis of cancer
predominance
● Control of magnetite properties by changing the particle size
● Effective incorporation with maintaining cell viability and cell function
● Utilization of function and target specificity of immune cells
● Effective incorporation with maintaining cell viability and cell function
● Utilization of function and target specificity of immune cells
application/development
● Cancer immunotherapy (magnetically mediated immunotherapy)
● Magnetic hyperthermia
● Magnetic resonance imaging
● Magnetic hyperthermia
● Magnetic resonance imaging
remarks
特許第5476620号「磁気微粒子包含細胞及びその製造方法」,発明者:逢坂哲彌,飯田広範,中西卓也,秋山靖人(静岡県立静岡がんセンター)
H. Iida, K. Takayanagi, T. Nakanishi, T. Osaka, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 314 (1), 274-280 (2007).
H. Iida, K. Takayanagi, T. Nakanishi, A. Kume, K. Muramatsu, Y. Kiyohara, Y. Akiyama, T. Osaka, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 101 (6), 1123-1128 (2008).
H. Iida, K. Takayanagi, T. Nakanishi, T. Osaka, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 314 (1), 274-280 (2007).
H. Iida, K. Takayanagi, T. Nakanishi, A. Kume, K. Muramatsu, Y. Kiyohara, Y. Akiyama, T. Osaka, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 101 (6), 1123-1128 (2008).
same researcher's seeds
-
 Field Effect Transistor Sensor
Field Effect Transistor Sensor
-
 Manufacturing of nano particle array substrates
Manufacturing of nano particle array substrates
-
 Hard-gold film technology for the realization of low-resistance and high mechanical strength
Hard-gold film technology for the realization of low-resistance and high mechanical strength
-
 All Wet ULSI manufacturing process
All Wet ULSI manufacturing process
-
 Evaluating lithium-ion battery (LIB) cell degradation using an impedance measurement
Evaluating lithium-ion battery (LIB) cell degradation using an impedance measurement
-
 Long-life negative silicon anode synthesis for next-generation lithium-ion batteries
Long-life negative silicon anode synthesis for next-generation lithium-ion batteries
-
 Production technology development for the creation of a next-generation laminated lithium-ion battery
Production technology development for the creation of a next-generation laminated lithium-ion battery
-
 Monitoring Chemical Balance in Epidermal Barriers
Monitoring Chemical Balance in Epidermal Barriers
-
 Development of Biosensing Technology for Food Safety
Development of Biosensing Technology for Food Safety
-
 Chemical Health Monitor Kind to Skin
Chemical Health Monitor Kind to Skin
-
 Seeing mental stress from invisible substances
Seeing mental stress from invisible substances
-
 Battery Diagnosis by Square-Current Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
Battery Diagnosis by Square-Current Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
posted:
2018/09/27