New pharmacological effects of thalidomide on neurons

- researcher's name
- affiliation
- research field
-
Neurochemistry/Neuropharmacology
- keyword
-
background
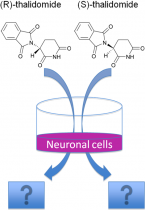
Thalidomide has a property known as chirality, meaning it has two enantiomers, R and S. While the R-enantiomer has a sedating effect, the S-enantiomer has side effects that cause teratogenicity in unborn children, so its administration is prohibited. However, a derivative of thalidomide (Lenalidomide© Celgene Corporation, etc.) has been drawing new attention in recent years as a drug of treatment for Hansen’s disease and multiple myeloma.
summary
The enantiomers, derivatives and metabolites of thalidomide are being analyzed to determine the various mechanisms of action in neurons by which they cause differences in pharmacological effect.
application/development
●Sedatives, anesthetics and other drugs that act on the nervous system can be considered in terms of administration conditions (focusing on their chirality) and drug modification to alleviate side effects.
●We are similarly examining their effects regarding the proteins that are involved in the development of neuropsychiatric disorders.
predominance
It is possible to propose methods of using and measuring the medical effects of physiologically-active substances that act on neurons, which take advantage of their chirality and other properties.
purpose of providing seeds
Sponsord research, Collaboration research, Technical consultation
same researcher's seeds
posted:
2014/05/21