New anti-Leishmania agent

- researcher's name
- affiliation
- research field
-
Biomolecular chemistry
- keyword
-
background
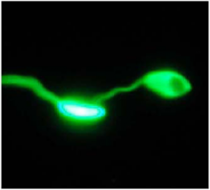
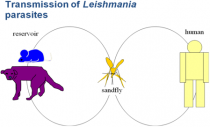
Leishmaniasis is a zoonotic, tropical infectious disease transmitted to humans through sandflies. It has infected 12 million people in 88 regions, and it is estimated that 2 million people become infected every year. Without treatment, leishmaniasis attacks the internal organs resulting in a 90% mortality rate.
summary
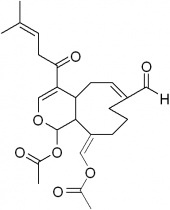
“Cristaxenicin A,” a new chemical compound with anti-Leishmania properties
application/development
The search for target molecules in the development of drugs to treat protozoan diseases, livestock drugs and other agents
predominance
Current treatments involve the use of antimony formulas, but it has side effects, and protozoans with resistance have begun to appear. Our chemical compound has a chemical structure that is completely different from traditional drugs, and it is believed to work through a totally different mechanism. It has high selective toxicity, and there are great expectations for it as an antiprotozoal drug with low toxicity.
purpose of providing seeds
Sponsord research, Collaboration research, Technical consultation
material
same researcher's seeds
posted:
2014/05/21