Activity change in the brain associated with pain relief
2021-0921-01

- researcher's name
-
about researcher ITO, Etsuro Professor
- affiliation
-
Faculty of Education and Integrated Arts and Sciences School of Education
- keyword
-
background
● It is so hard to identify the causes of chronic pain, and thus to relieve the pain, complementary and alternative medicine is required.
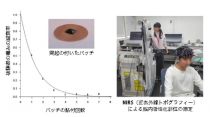
● We have so far found that adhesion of pyramidal thorn patches on the pain region is effective for pain relief.
● Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) was used to identify the brain region that was changed by the patch treatment.
Then, we hypothesized that if this brain region could be activated/inactivated, the pain would be relieved.
summary
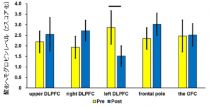
● The oxyhemoglobin levels of lDLPFC became down, i.e., the activity was suppressed, during pain relief.
predominance
● When we can suppress the activity of lDLPFC by exogenous stimuli, we can escape from drug ment, which is not expected to have a large effect. Consequently, the side effects are suppressed and the medical costs are cut down.
application/development
● What kind of stimulus can inactivate the lDLPFC activity?
● Development to pharmaceutical industry.
● Cooperation with psychology.
same researcher's seeds
-
 Development of new diagnosis using ultrasensitive ELISA
Development of new diagnosis using ultrasensitive ELISA -
 Ultrasensitive antigen test for COVID-19
Ultrasensitive antigen test for COVID-19 -
 Sins of anticancer drugs
Sins of anticancer drugs
posted:
2021/10/08