Method for monitoring the treatment effect of Myeloproliferative neoplasms
2019-1021-08

- researcher's name
-
about researcher TSUNEDA, Satoshi Professor
- affiliation
-
Faculty of Science and Engineering
- research field
-
Biofunction/Bioprocess,Environmental engineering and reduction of environmental burden,Applied microbiology,Bacteriology (including mycology)
- keyword
-
background
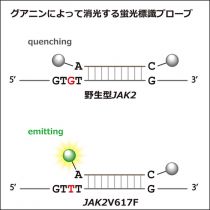
● JAK2 V617F point mutation is detected as one of the driver mutations of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs)
● High JAK2 V617F allele burden associates with the poor prognosis of MPNs
● Clinical examination technique to estimate the therapeutic effects is required
● High JAK2 V617F allele burden associates with the poor prognosis of MPNs
● Clinical examination technique to estimate the therapeutic effects is required
summary
● Usage of the fluorescence-dye-labeled probe exhibiting fluorescent intensity as a function of the amount of V617F allele
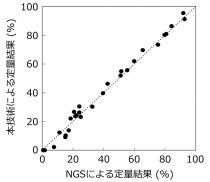
● JAK2 V617F allele burden can be quantified equivalent to the results by next- generation sequencing (NGS)
● Available for the monitoring of slight increase/decrease of V617F allele burden
● JAK2 V617F allele burden can be quantified equivalent to the results by next- generation sequencing (NGS)
● Available for the monitoring of slight increase/decrease of V617F allele burden
predominance
● NGS-compatible determination precision with simple and cost-effective workflow
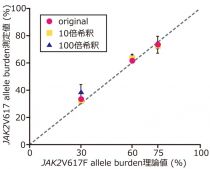
● Precise quantification independent with the input gDNA amount
● Utilized to determine the therapeutic effect
● Precise quantification independent with the input gDNA amount
● Utilized to determine the therapeutic effect
application/development
● Clinical examination
● Prognosis predicting
● Drug screening
● Prognosis predicting
● Drug screening
same researcher's seeds
-
 Diagnostic method for chronic myeloproliferative diseases – method for quantitatively analyzing the JAK2 genetic mutation –
Diagnostic method for chronic myeloproliferative diseases – method for quantitatively analyzing the JAK2 genetic mutation – -
 New isolation and culturing method for microorganisms
New isolation and culturing method for microorganisms -
 Mutational analysis method for JAK2 genes
Mutational analysis method for JAK2 genes
posted:
2019/10/21