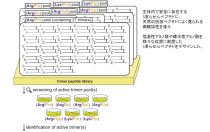
Novel antimicrobial peptides
2015-1023-03

- researcher's name
-
about researcher KOIDE, Takaki Professor
- affiliation
-
Faculty of Science and Engineering
- research field
-
Structural biochemistry,Drug development chemistry,Biomolecular chemistry
- keyword
-
background
・ The development of new antibacterial agents was demanded because of increasing threat of multi-drug resistant bacteria.
・ Conventional antimicrobial peptides are readily degraded by proteases.
・ Conventional antimicrobial peptides are readily degraded by proteases.
summary
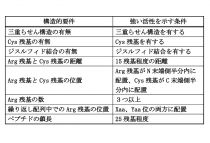
Novel antimicrobial peptides which form triple-helical structure and contain Arg cluster in the N-terminal region and disulfide bonds in the C-terminal region.
predominance
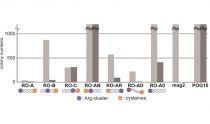
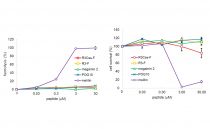
・ This peptide inhibited E. coli growth by a different mechanism from that of low molecular-weight antibiotics.
・ Remarkably stability in human serum.
・ More potent antimicrobial activity than magainin 2.
・ Low hemolytic and cytotoxic activities.
・ Remarkably stability in human serum.
・ More potent antimicrobial activity than magainin 2.
・ Low hemolytic and cytotoxic activities.
application/development
Orally administration for treating intestinal tract, intravenous administration for urinary tract infection,and antibacterial eye lotion, etc.
material
same researcher's seeds
-
 Drug development based on collagen
Drug development based on collagen -
 Collagen-like Peptide Polymer with Gelating Property
Collagen-like Peptide Polymer with Gelating Property -
 An artificial collagen-like material based on triple helix-forming peptides
An artificial collagen-like material based on triple helix-forming peptides -
 Probes for theranostics that target denatured collagen
Probes for theranostics that target denatured collagen
posted:
2015/10/23