Heat extraction rate maximized by the use of nanofluid in heat exchangers
2012-0313-02

- researcher's name
-
about researcher MOROOKA, Shinichi Professor (retired)
- affiliation
-
Faculty of Science and Engineering Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering
- keyword
-
background
Smaller designs are needed to raise the economic potential of heat exchangers (steam generators) that produce steam in order to convey outside, the heat removed from nuclear reactors.
summary
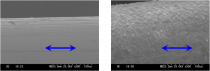
Mixing TiO2 nanoparticles into the media (water) inside a heat exchanger and conducting several hours of preliminary steam generator operation, causes the nanofluid to adsorb onto the inside of the heat transfer tube and a nanostructure to be formed. So doing increases the heat extraction rate.
application/development
The same process can also be applied to general heat exchangers that use steam, such as boiler heat transfer pipes and air conditioner evaporators
predominance
By making use of nanoparticles, it becomes possible to obtain results through short-term operation, without having to mechanically process heat transfer tubes. Additionally, they are low in cost.
purpose of providing seeds
Sponsord research, Collaboration research, Technical consultation
posted:
2014/05/21