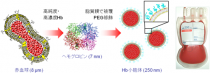
Artificial red blood cell production method
2011-1027-01

- researcher's name
-
about researcher SAKAI, Hiromi Guest Senior Researcher (retired)
- affiliation
-
Research Council (Research Organization) Organization for University Research Initiatives
- keyword
-
background
Japan’s blood transfusion system is of the global highest standard, but problems remain from the perspective of dealing with blood type and infection sources, risk management during disasters and more.
Artificial blood has the potential to resolve these problems in the field of blood transfusion in one fell swoop.
summary
Production method for artificial red blood cells with the hemoglobin that binds to oxygen encapsulated in a lipid membrane.
Demonstrated benefits include: (a) No blood types, (b) viruses and other infection sources are removed, (c) stable at room temperature for at least two years, (d) broken down and excreted by the metabolic system even when given in large amounts, (e) uniformly dispersed in plasma, to supply oxygen to the peripheral tissues where red blood cells cannot reach, (f) is safe and has the same oxygen delivery effects as red blood cells as a resuscitative fluid to treat hemorrhagic shock.
application/development
●Diseases that cannot be treated with a transfusion, ischemic diseases, cancer treatment, etc.
●Use in oxygen storage solutions and regenerative medicine, by using the oxygen supplying capacity
●CO gas carrier with cell-protective effects
predominance
It is chemically stable and can be stored at room temperature for at least two years. Technology for adjusting the physical values including particle size, oxygen affinity and viscosity is growing.
Safety and efficacy have been confirmed in animal experiments (rats, hamsters, beagles (dog), crab-eating macaque).
Development of constructive manufacturing methods, with a view to eventual, industrial production, has advanced.
purpose of providing seeds
Sponsord research, Collaboration research, Technical consultation
posted:
2014/05/21